Exposure to Noise

Sound is an oscillation transmitted in an elastic medium without carrying material, but only energy.
Noise is an unwanted signal of natural or artificial origin.
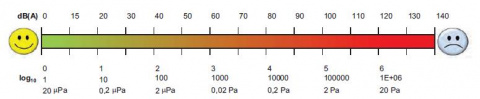
Sound pressure levels are conventionally measured in decibels (dB).
Noise can affect health in several ways, and even result in hearing loss.
It may also affect safety: noise can produce a masking effect, interfering with the ability to hear warning signals.
Chapter II, Title VIII of Legislative Decree 81 of 9 April 2008 establishes measures for preventing and protecting against noise exposure in the workplace, especially for preventing hearing loss.
Art. 190 of Legislative Decree 81/2008 establishes the requirement for employers to measure noise levels in the workplace in order to identify workers exposed to this hazard and implement the appropriate preventive and health protection measures.
The risk assessment must be performed by a qualified person at all undertakings with employees or workers treated as such, irrespective of the production sector; where it cannot reasonably be excluded that lower exposure action values may be exceeded (LEX>80 dB(A) or Lpeak,C > 135 dB(C)) the assessment must also include measurements performed in accordance with the relevant technical standards (UNI EN ISO 9612:2011 and UNI 9432:2011).
WHAT TO DO when you intend to buy new equipment that is noisy
If you intend to purchase such equipment, you must notify the Health and Safety Services Unit (PREP), attaching the technical data sheet of the equipment and stating the name of the laboratory where it will be used. The Health and Safety Services Unit will assess the risk directly using a sound-level meter and, where applicable:
- design sound-absorbing shields to reduce structure-borne noise;
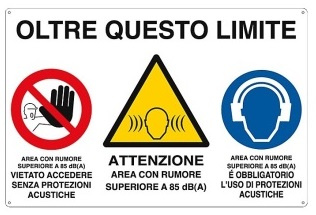
- define a “restricted access area” and mark this with appropriate safety signs;
- instruct users on suitable personal protective equipment to be used.